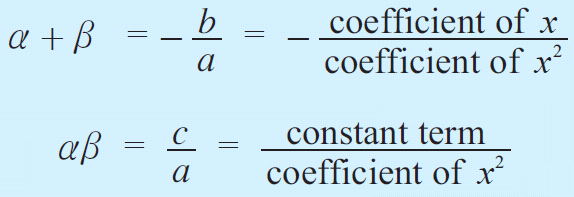
If a quadratic equation is given in standard form, we can find the sum and product of the roots using coefficient of x 2 , x and constant term.
Let us consider the standard form of a quadratic equation,
(a, b and c are real and rational numbers)
Let α and β be the two zeros of the above quadratic equation.
Then the formula to get sum and product of the roots of a quadratic equation :
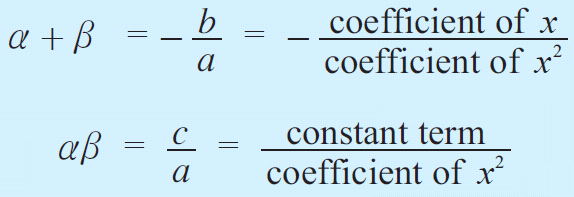
Irrational roots of a quadratic equation occur in conjugate pairs.
That is, if (m + √n) is a root, then (m - √n) is the other root of the same quadratic equation equation.
Form the quadratic equation whose roots are 2 and 3.
Sum of the roots is
Product of the roots is
Formation of quadratic equation :
x 2 - (sum of the roots)x + product of the roots = 0
Form the quadratic equation whose roots are 1/4 and -1.
Sum of the roots is
Product of the roots is
Formation of quadratic equation :
x 2 - (sum of the roots)x + product of the roots = 0
x 2 - (-3/4)x + (-1/4) = 0
x 2 + (3/4)x - 1/4 = 0
Multiply each side by 4.
Form the quadratic equation whose roots are 2/3 and 5/2.
Sum of the roots is
The least common multiplication of the denominators 3 and 2 is 6.
Make each denominator as 6 using multiplication.
Product of the roots is
Formation of quadratic equation :
x 2 - (sum of the roots)x + product of the roots = 0
x 2 - (19/6)x + 5/3 = 0
Multiply each side by 6.
6x 2 - 19x + 10 = 0
If one root of a quadratic equation (2 + √3), then form the equation given that the roots are irrational.
(2 + √3) is an irrational number.
We already know the fact that irrational roots of a quadratic equation will occur in conjugate pairs.
That is, if (2 + √3) is one root of a quadratic equation, then (2 - √3) will be the other root of the same equation.
So, (2 + √3) and (2 - √3) are the roots of the required quadratic equation.
Sum of the roots is
Product of the roots is
Formation of quadratic equation :
x 2 - (sum of the roots)x + product of the roots = 0
If α and β be the roots of x 2 + 7x + 12 = 0, find the quadratic equation whose roots are
( α + β) 2 and (α - β) 2
Given : α and β be the roots of x 2 + 7x + 12 = 0.
sum of roots = -coefficient of x/coefficient of x 2
product of roots = constant term/coefficient of x 2
Quadratic equation with roots ( α + β) 2 and (α - β) 2 is
x 2 - [ ( α + β) 2 + (α - β) 2 ]x + ( α + β) 2 (α - β) 2 = 0 ----(1)
Find the values of ( α + β) 2 and ( α - β) 2 .
( α - β) 2 = (α + β) 2 - 4αβ
( α - β) 2 = (-7) 2 - 4(12)
So, the required quadratic equation is
(1)----> x 2 - [49 + 1]x + 49 ⋅ 1 = 0
x 2 - 50x + 49 = 0
If α and β be the roots of x 2 + px + q = 0, find the quadratic equation whose roots are
Given : α and β be the roots of x 2 + px + q = 0.
sum of roots = -coefficient of x/coefficient of x 2
product of roots = constant term/coefficient of x 2
Quadratic equation with roots α/β and β/α is
x 2 - (α/β + β/α)x + ( α/β)(β/α) = 0
x 2 - [α/β + β/α]x + 1 = 0 ----(1)
Find the value of (α/β + β/α).
α/β + β/α = α 2 /αβ + β 2 /αβ
So, the required quadratic equation is
(1)----> x 2 -[ (p 2 - 2q)/q ]x + 1 = 0
Multiply each side by q.
qx 2 - (p 2 - 2q) x + q = 0
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
© All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com